Vision System
Vision System technology is integral to modern robotic automation, enabling robots to perceive and interact with their environment in sophisticated ways. A Vision System combines hardware and software to capture, process, and analyze visual information, allowing robots to perform tasks with high precision and autonomy.
Key Components of Robotic Vision Systems
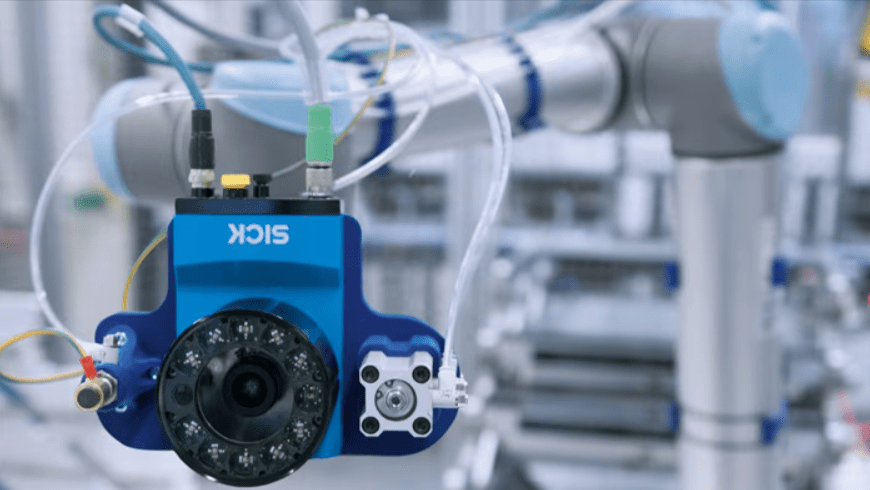

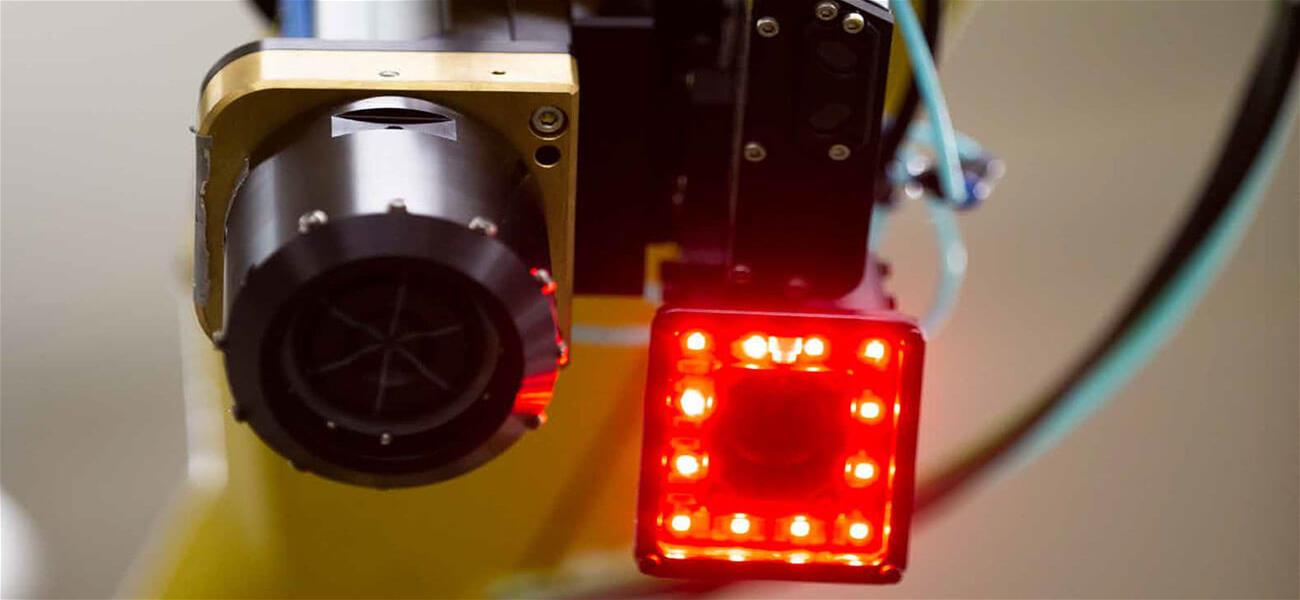
Cameras
- Types: Vision System components include CCD (Charge-Coupled Device), CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor), 3D cameras, and stereo cameras.
- Function: A Vision System captures images or video of the robot’s environment for processing and analysis.
- Application: Vision System is used for object detection, identification, and navigation in automated industrial setups.
Lighting
- Types: LED lights, ring lights, backlights, and structured light projectors.
- Function: Provide consistent illumination to enhance image quality.
- Application: Essential for maintaining image clarity and reducing shadows or reflections.
Image Processing Software
- Function: Analyzes the captured images to extract useful information.
- Application: Includes tasks like object recognition, feature extraction, and defect detection.
Sensors
- Types: LIDAR, ultrasonic sensors, and infrared sensors.
- Function: Supplement visual data with additional spatial and depth information.
- Application: Enhances the accuracy and reliability of the vision system.
Computing Hardware
- Types: GPUs, CPUs, and edge devices.
- Function: Perform the computational tasks required for real-time image processing and analysis.
- Application: Enables rapid processing of complex algorithms for immediate feedback and action.
Applications of Robotic Vision Systems
Quality Inspection
- Tasks: Detect defects, measure dimensions, and verify the integrity of products.
- Industries: Manufacturing, electronics, automotive, and pharmaceuticals.
- Benefits: Ensures consistent product quality and reduces manual inspection costs.
Pick and Place
- Tasks: Identify and grasp objects from various positions and orientations.
- Industries: Warehousing, logistics, and assembly lines.
- Benefits: Increases speed and accuracy in sorting and assembly operations.
Palletizing and Depalletizing
- Tasks: Rapidly fulfill orders and restock shelves to meet fast-changing demand.
- Industries: Efficiently manage bulk packaging, handling perishable goods quickly to prevent spoilage.
- Benefits: Speeds up the loading and unloading of goods, reducing manual effort and time.
Object Recognition and Sorting
- Tasks: Identify and classify objects based on size, shape, color, or barcode.
- Industries: Recycling, food processing, and e-commerce.
- Benefits: Automates sorting processes, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
Assembly Verification
- Tasks: Ensure correct assembly of components, detect missing or misaligned parts.
- Industries: Electronics, automotive, and consumer goods.
- Benefits: Reduces rework and ensures the reliability of assembled products.
Mahajan Automation, Empowering Automation with Advanced Vision Systems for Superior Accuracy and Efficiency
Benefits of Robotic Vision Systems
Increased Precision and Accuracy
- Explanation: Vision systems provide high-resolution images and precise measurements.
- Application: Ensures accurate positioning and quality control in various tasks.
Enhanced Flexibility
- Explanation: Robots can adapt to different tasks and environments without extensive reprogramming.
- Application: Useful in dynamic industries where product lines frequently change.
Improved Safety
- Explanation: Robots can detect and avoid obstacles or hazardous conditions.
- Application: Reduces the risk of accidents in industrial settings.
Cost Savings
- Explanation: Automates manual tasks, reducing labor costs and increasing throughput.
- Application: Leads to long-term cost efficiency and higher return on investment.
Real-Time Decision Making
- Explanation: Vision systems provide immediate feedback, allowing for on-the-fly adjustments.
- Application: Improves process efficiency and responsiveness
What We Do
“A compelling way of generating innovative ideas”
Visual feedback is essential for image and vision-guided robots. Their power of sight is one of the elements that make them widely used across different disciplines.
Welding Seams in Welding Systems
Fully automated welding places great demands on quality and precision. Consequently, the correct position of the respective seam must be reliably detected before the welding process is started in the robot cell. Welding systems are equipped with innovative weCat3D 2D/3D profile sensors for the purpose of weld seam tracking.
- Image Processing
- Part Inspection
- De-Palletization and primary packaging
- Welding Seam Tracking
- Sorting
Solutions of Robotic Vision Systems
High Initial Investment
Emphasize long-term benefits and potential cost savings.
Complex Integration
Detailed planning and collaboration with experienced integrators.
Lighting Variability
Use consistent lighting solutions and adaptive image processing algorithms.
Processing Speed
Employ powerful computing hardware and optimized algorithms.
Data Management
Implement efficient data storage and processing solutions, leveraging cloud and edge computing.